Have you ever wondered how much it costs to get your ad seen by 1,000 eyes in the vast digital landscape? If so, then you’ve likely encountered the term CPM, or Cost Per Mille.
For a beginner navigating the world of online advertising, CPM can seem like a confusing acronym shrouded in mystery. But fear not, this guide aims to shine a light on CPM, making it an easily understood and valuable tool in your advertising arsenal.
What Exactly is CPM?
In simpler terms, it’s the cost you pay for every 1,000 impressions your ad receives. An impression simply means the number of times your ad appears on a website, app, or other online platform.
Why do we calculate CPM?
Well, it offers several key benefits for marketers:
#1. Increased Brand Awareness: By putting your ad in front of thousands of potential customers, you can significantly boost brand recognition and build familiarity with your offerings.
#2. Reach Targeted Audiences: With careful targeting options, you can ensure your ad reaches people most likely to be interested in your product or service, maximizing your ad spend.
#3. Predictable Budgeting: Unlike other pricing models, CPM offers more predictable costs, allowing you to set a budget and know exactly how many impressions you’ll get for your money.
But before you hop on the CPM bandwagon, it’s crucial to understand that it’s not without its drawbacks:
- No Guarantees: Just because your ad is seen, doesn’t mean it will be clicked or lead to a conversion.
- Potential for High Costs: CPM rates can vary greatly depending on several factors, and you might end up paying a high price for impressions that don’t translate to engagement.
- Indirect ROI Measurement: Unlike models like Cost Per Click (CPC) or Cost Per Acquisition (CPA), measuring the direct return on investment for CPM campaigns can be more challenging.
Don’t worry, we’ll delve deeper into these pros and cons later! In the next section, we’ll unpack the nitty-gritty of CPM calculations and factors influencing costs. Stay tuned as we unravel the mysteries of CPM together!
Understanding CPM Calculations and Costs
Now that we’ve demystified the basic concept of CPM, let’s dive into the numbers and understand how Cost Per Mille is calculated and what influences its cost.
The Formula:
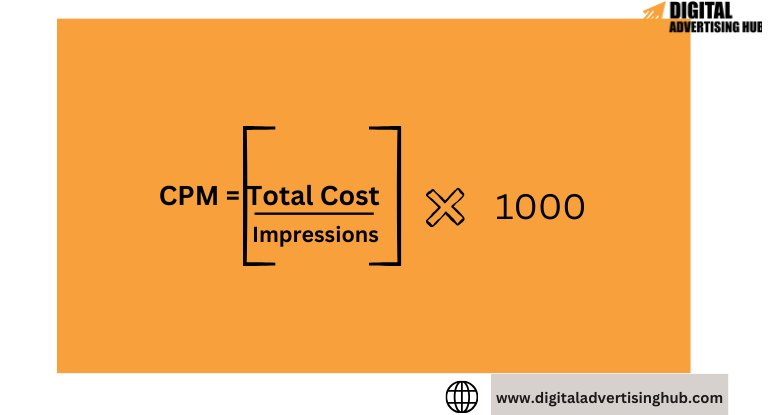
Calculating CPM boils down to this simple formula:
CPM = Total Cost / Impressions * 1,000
So, if you spent $20 for 5,000 impressions, your CPM would be:
CPM = $20 / 5,000 impressions * 1,000 = $4
This means you paid $4 to get your ad seen by 1,000 people. Simple, right?
But hold on, there are several factors that can influence the cost you pay per impression.
Factors That Can Influence CPM
#1. Website Traffic:
High-traffic websites with engaged audiences typically command higher CPM rates because advertisers value the opportunity to reach a larger number of potential customers.
Websites that consistently attract a significant volume of visitors and offer engaging content tend to have higher demand for ad space, leading to increased competition among advertisers and higher CPM rates.
#2. Audience Targeting:
Narrowly targeting specific demographics or interests can increase CPM rates because advertisers value the ability to reach a highly relevant audience.
When advertisers target a specific segment of the population with precise demographic, behavioral, or interest-based criteria, they can deliver more personalized and tailored advertising messages, resulting in higher engagement and conversion rates.
#3. Ad Format:
The format of the ad also plays a significant role in determining CPM rates. Eye-catching and interactive ad formats, such as video ads or rich media ads, typically cost more than simple banner ads or text-based ads.
Video ads, in particular, require more resources to produce and tend to capture users’ attention more effectively, making them a preferred choice for many advertisers.
#4 Device Targeting:
Targeting specific devices, such as mobile devices or desktop computers, can also impact CPM rates. In recent years, mobile usage has surged, with more people accessing the internet and consuming content on their smartphones and tablets.
As a result, targeting mobile devices might be more expensive than desktop due to the higher usage frequency and increased competition for ad space on mobile platforms.
#5. Seasonality and Competition:
Certain times of year and industries experience higher competition among advertisers, leading to fluctuations in CPM rates. Seasonal events, holidays, and peak shopping periods can drive up demand for advertising inventory, resulting in higher CPM rates. Additionally, industries with intense competition or high demand for advertising space may see higher CPM rates year-round.
By understanding these factors and their impact on CPM rates, you can make informed decisions about your advertising strategies, optimize campaign performance, and maximize ROI.
Considering website traffic, audience targeting, ad format, device targeting, seasonality and competition allows you to tailor your campaigns effectively to reach your target audience and achieve your marketing objectives.
How to Set Your Budget

Setting an effective CPM (Cost Per Mille) budget requires careful consideration of campaign objectives, industry benchmarks, and available resources. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to set a budget that aligns with your goals and maximizes campaign effectiveness:
#1. Define your goals:
Before determining your CPM budget, it’s essential to clearly define your campaign goals. Ask yourself: Are you primarily focused on increasing brand awareness, driving website traffic, or generating conversions? Your goals will dictate the value you place on each impression and how much you’re willing to pay to achieve them.
For example, if your goal is to increase brand awareness, you may prioritize reaching a broad audience with your ads and be willing to pay a higher CPM rate for increased visibility.
On the other hand, if your goal is to drive clicks or conversions, you may be more conservative with your CPM budget and focus on targeting a smaller, more engaged audience.
#2. Research benchmarks:
Before setting your CPM budget, it’s essential to research industry benchmarks and average CPM rates for your specific industry and target audience. Analyzing this data will help you set realistic expectations and ensure that your budget aligns with market norms.
For instance, if you’re in the fashion retail industry targeting millennial women, research average CPM rates for similar campaigns in your industry and demographic. This information will give you a baseline for understanding typical costs and help you gauge the competitiveness of your budget.
#3. Start small and experiment:
When setting your CPM budget, it’s wise to start small and experiment with different budget levels to assess campaign performance and gather insights. Begin with a conservative budget that allows for testing and optimization, then gradually scale up based on results and learnings.
Suppose you’re launching a new product and running a CPM campaign to generate awareness. Start with a modest budget and monitor key performance metrics such as impressions, click-through rates, and conversions. Based on the initial results, you can adjust your budget allocation and targeting strategies to optimize performance over time.
By following these tips and considering your campaign goals, industry benchmarks, and budget constraints, you can set an effective CPM budget that maximizes the impact of your advertising efforts.
Making informed decisions about your CPM campaigns will set you up for success and ensure that you achieve your marketing objectives efficiently.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using CPM?

Having grasped the mechanics of CPM, let’s now dissect its strengths and weaknesses to help you decide if it’s the right fit for your marketing goals.
Advantages
#1. Boost Brand Awareness: If your primary objective is building brand recognition and reaching a large audience, it is the best option. With every thousand impressions, your brand message lands on potential customers’ screens, fostering familiarity and recall.
#2. Predictable Budgeting: Unlike models like CPC, where costs fluctuate based on clicks, CPM offers upfront cost clarity. You set your budget and know exactly how many impressions you’ll receive, simplifying campaign planning and resource allocation.
#3. Flexibility in Targeting: Platforms offer robust targeting options, allowing you to reach specific demographics, interests, and even locations, ensuring your ad reaches the most relevant audience.
#4. Branding Opportunities: Certain ad formats, like video or premium placements, can enhance brand image and create impactful experiences, strengthening brand perception.
Disadvantages
#1. No Guarantee of Engagement: While impressions are valuable, they don’t guarantee clicks or conversions. You might end up paying for views that don’t translate to actual interest or action.
#2. Potential for High Costs: Depending on targeting and platform, CPM rates can escalate, leading to expensive impressions with limited ROI, especially for low-engagement campaigns.
#3. Indirect ROI Measurement: Unlike CPC or CPA, directly measuring the return on investment for CPM campaigns can be trickier. You need to factor in brand awareness uplift and long-term impact, which can be difficult to quantify.
#4. Limited Control over Clicks: You don’t directly control how many people click on your ad, making it a less targeted approach compared to models based on user actions.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Choosing the right pricing model depends on your campaign goals and budget. If visibility and brand awareness are paramount, CPM offers a cost-effective way to reach a large audience. However, if immediate conversions or ROI measurements are crucial, alternatives like CPC or CPA might be more suitable.
Before you decide, carefully consider your objectives, target audience, and budget constraints. In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into best practices for optimizing your CPM campaigns and extracting maximum value!
Best Practices for Optimizing CPM Campaigns
Now that you understand the advantages and disadvantages of CPM, let’s explore strategies to ensure your campaigns deliver optimal results.
#1. Refine Your Targeting
- Demographics: Go beyond basic demographics and leverage interests, behaviors, and purchase intent to reach highly relevant audiences.
- Contextual Targeting: Align your ads with content relevant to your audience’s interests, increasing ad resonance and potential engagement.
- Device Targeting: Optimize ad formats and targeting based on the devices your audience uses most frequently.
#2. Choose the Right Ad Format
- Banner Ads: Cost-effective for basic brand awareness.
- Video Ads: Captivate audiences with engaging stories and drive higher engagement.
- Native Ads: Seamlessly blend with website content, offering a less intrusive experience.
- Rich Media Ads: Interactive elements can attract attention and boost engagement.
#3. A/B Test Creatives
- Experiment with different visuals, headlines, and copy to see what resonates best with your target audience.
- Track performance metrics like click-through rates and engagement to identify winning creatives.
- Continuously optimize your ad content based on data-driven insights.
#4. Monitor and Analyze Performance:
- Regularly track key metrics like impressions, clicks, cost per click (CPC), and engagement rates.
- Analyze how different placements and targeting options perform to identify areas for improvement.
- Leverage platform insights and reporting tools to gain deeper understanding of your audience and campaign effectiveness.
#5. Set Clear Goals and Expectations:
- Define what success looks like for your campaign, be it website visits, brand mentions, or lead generation.
- Set realistic goals based on your budget and target audience.
- Track progress toward your goals and adjust your campaign accordingly.
You should always remember that optimization is an ongoing process: Continuously monitor, analyze, and refine your campaign based on data and performance.
Many platforms offer automated bidding tools that can optimize CPM based on your goals and budget. Keep up with industry trends and best practices to ensure your CPM strategies remain effective.
By following these best practices, you can make informed decisions, optimize your CPM campaigns, and maximize your return on investment.
Conclusion
We’ve journeyed through the world of CPM, unraveling its mechanics, advantages, drawbacks, and best practices. Remember, CPM isn’t a magic bullet, but a valuable tool in your marketing toolkit when used strategically.
Key Takeaways:
- CPM offers a cost-effective way to reach a large audience and build brand awareness.
- Carefully consider your goals and target audience before choosing CPM.
- Optimize your campaigns with refined targeting, impactful ad formats, and data-driven decisions.
- Track performance, set clear goals, and embrace automation to maximize your ROI.
It is worthy to remember that CPM shines for brand awareness and reach, but consider alternatives like CPC or CPA for direct action campaigns. Experiment, analyze, and refine to unlock the full potential of CPM.
Ready to put your CPM knowledge into action? Start experimenting with targeted campaigns, A/B testing creatives, and utilizing data-driven insights to optimize your efforts. As you navigate the digital landscape, remember that CPM can be a powerful ally in achieving your marketing goals.










